
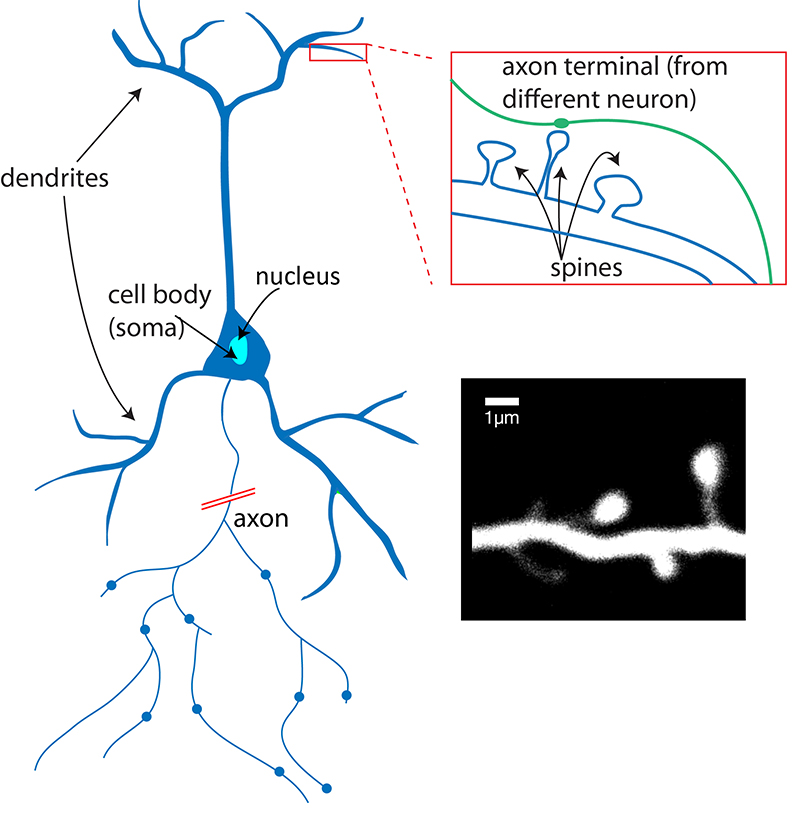

Compare with F, G that show distinct neurons. Figure 12.2.1 – The variety of neuron shapes found in the brain: Note, letters B and C show star shaped neurons without axons. Some neurons have a single long extension (axon) that reaches great distances, others are very small, star shaped cells without obvious axons (See Figure 12.2.1 – add to image the term axon, reference cells without one). Neurons are nucleated cells with specialized structural properties. Ongoing research also suggests that glial cell number matches neuron number and that they even can send signals themselves. Glial cells maintain the extracellular environment around neurons, improve signal conduction in neurons and protect them from pathogens. Glial cells, or glia or neuroglia, are much smaller than neurons and play a supporting role for nervous tissue. They are electrically active and release chemical signals to communicate between each other and with target cells. Neurons are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. List the glial cells of the PNS and describe their function.List the glial cells of the CNS and describe their function.Identify the different types of neurons on the basis of shape.Describe the basic structure of a neuron and how these structures function in a neuron.By the end of this section, you will be able to:Įxplain how neurons and glial cells work together to perform and support the nervous system functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
